filler
filler
IMIB research
filler
filler
Understanding antibiotic resistance is one of the most pressing challenges in modern medicine, and Staphylococcus aureus, a major bacterial pathogen, is at the forefront of this battle. S. aureus is one of the leading causes of both community-acquired and hospital-acquired infections, ranging from mild skin infections to life-threatening conditions such as pneumonia, sepsis, and endocarditis. A critical aspect of S. aureus pathogenesis is its ability to survive and replicate both extracellularly and intracellularly, allowing it to evade the host immune response and establish persistent infections. Our research focuses on different aspects of this dynamic interplay.
filler
If any of these topics interest you reach out!
filler
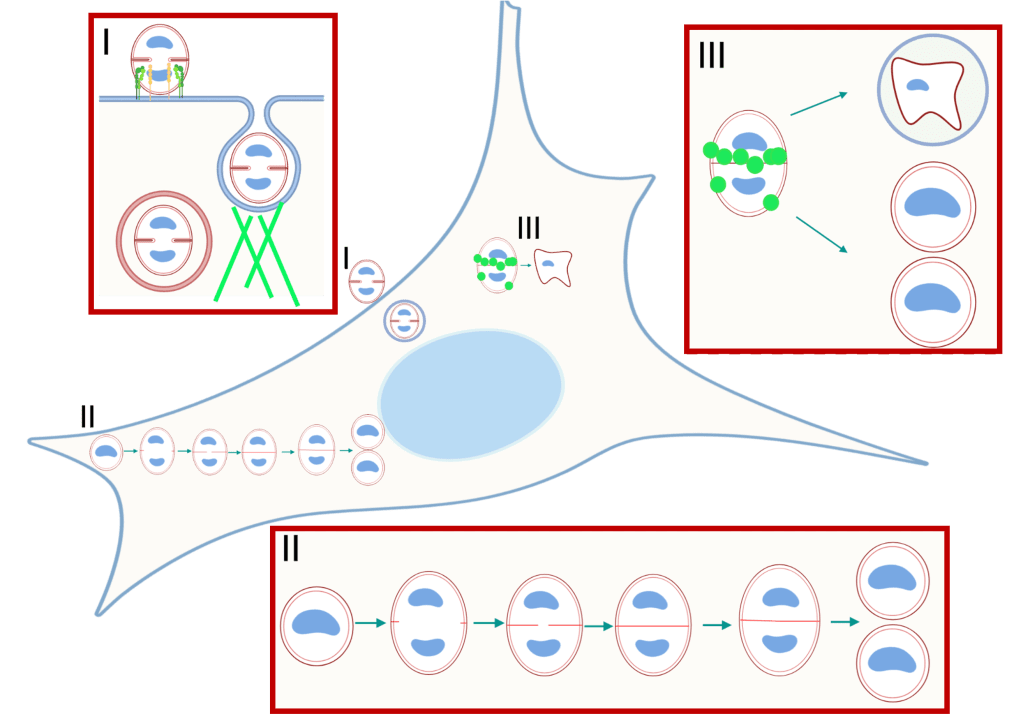
Unraveling S. aureus lifestyle switch: Our research aims to elucidate the mechanisms that allow S. aureus to transition between its extracellular and intracellular lifestyles.
filler
filler
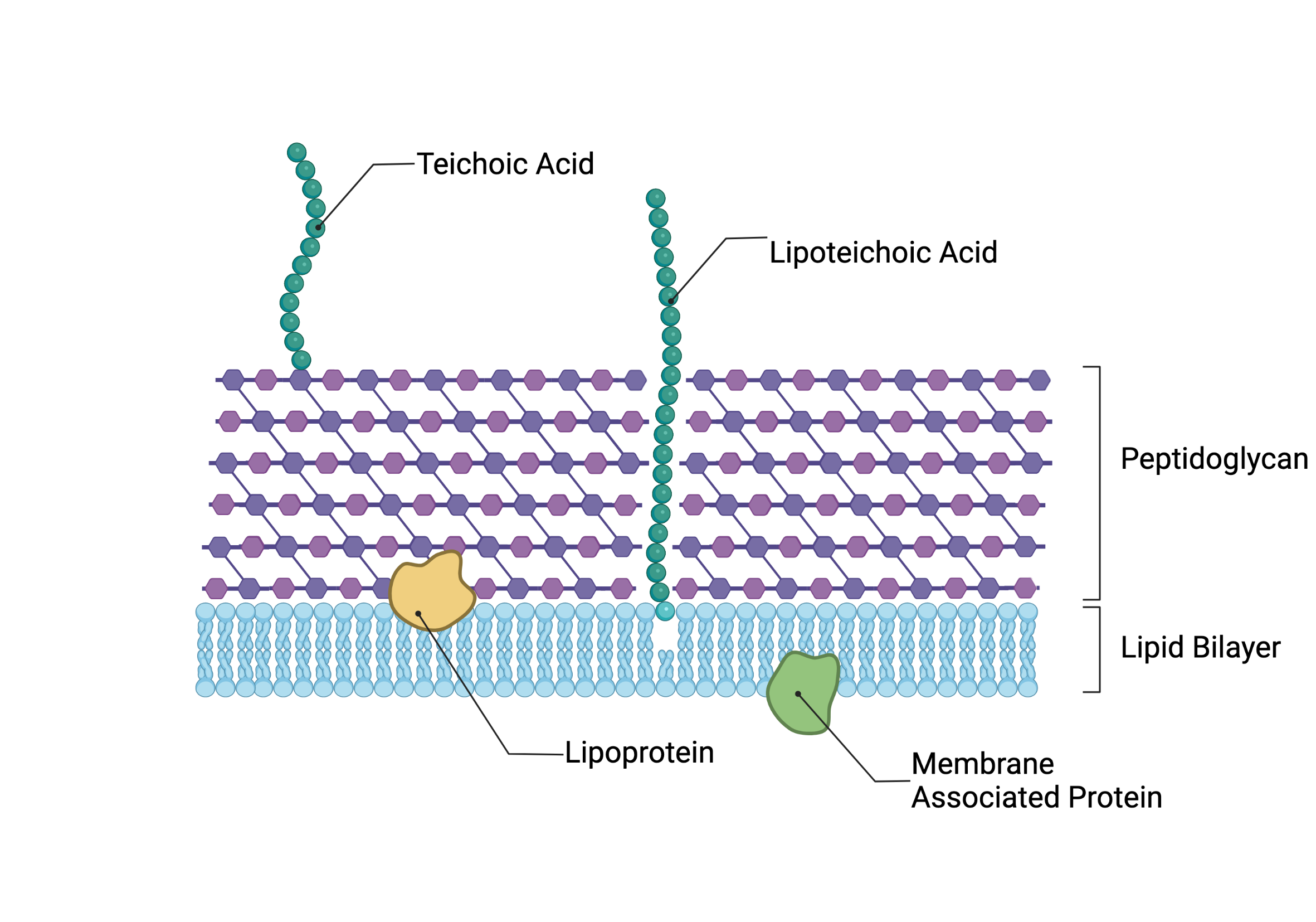
S. aureus intracellular immune evasion: We are investigating the bacterial factors that are recognized by host cells during intracellular infection and the strategies employed by S. aureus to avoid detection.
filler
filler
Host factors in S. aureus recognition: Our goal is to identify and characterize the host factors responsible for detecting intracellular S. aureus.
filler
Organ-on-chip models for infection: We are developing advanced in vitro models that better recapitulate the characteristics of human tissues, such as organ-on-chip systems, taking into account factors like tissue architecture, fluid flow, and the presence of multiple cell types.
filler

filler
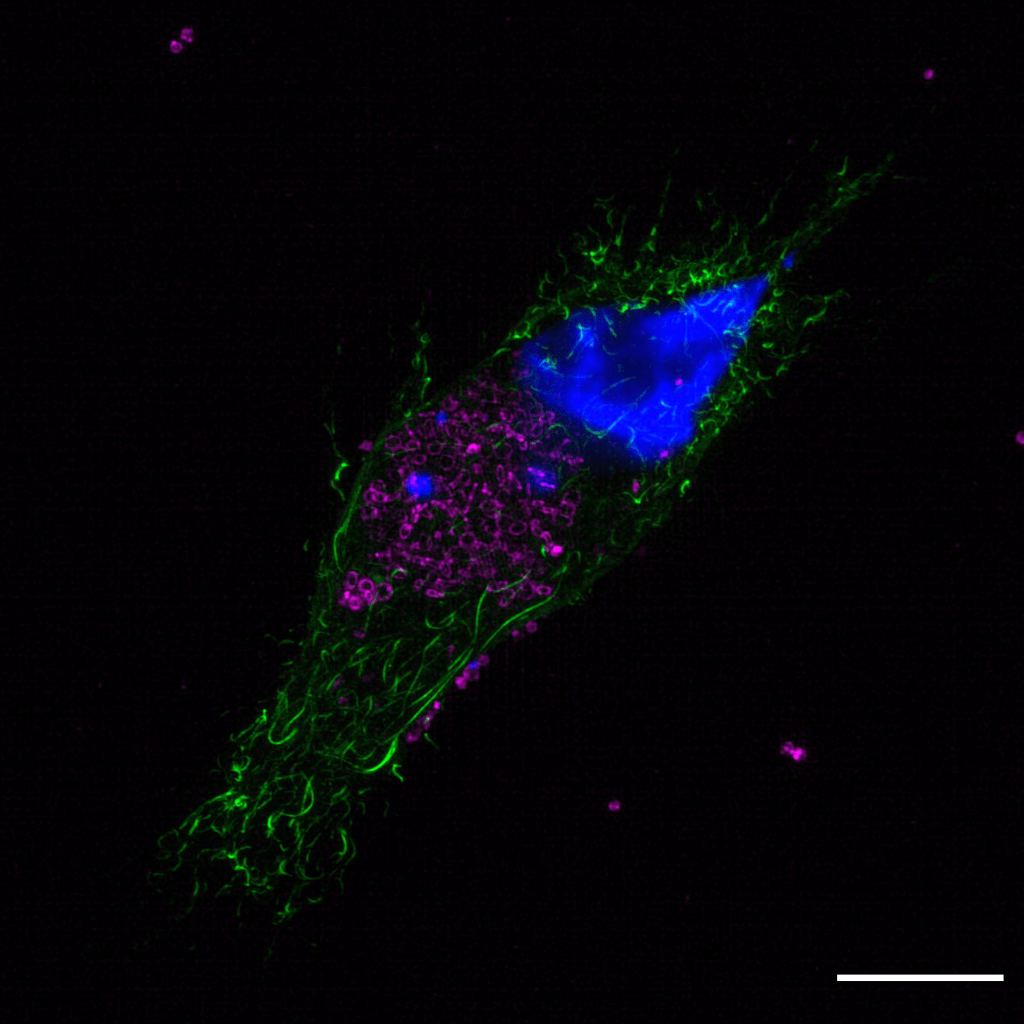
Advanced microscopy techniques for infection dynamics: We are using and developing state-of-the-art microscopy-based solutions to gain a deeper understanding of the spatiotemporal dynamics of S. aureus intracellular infection.
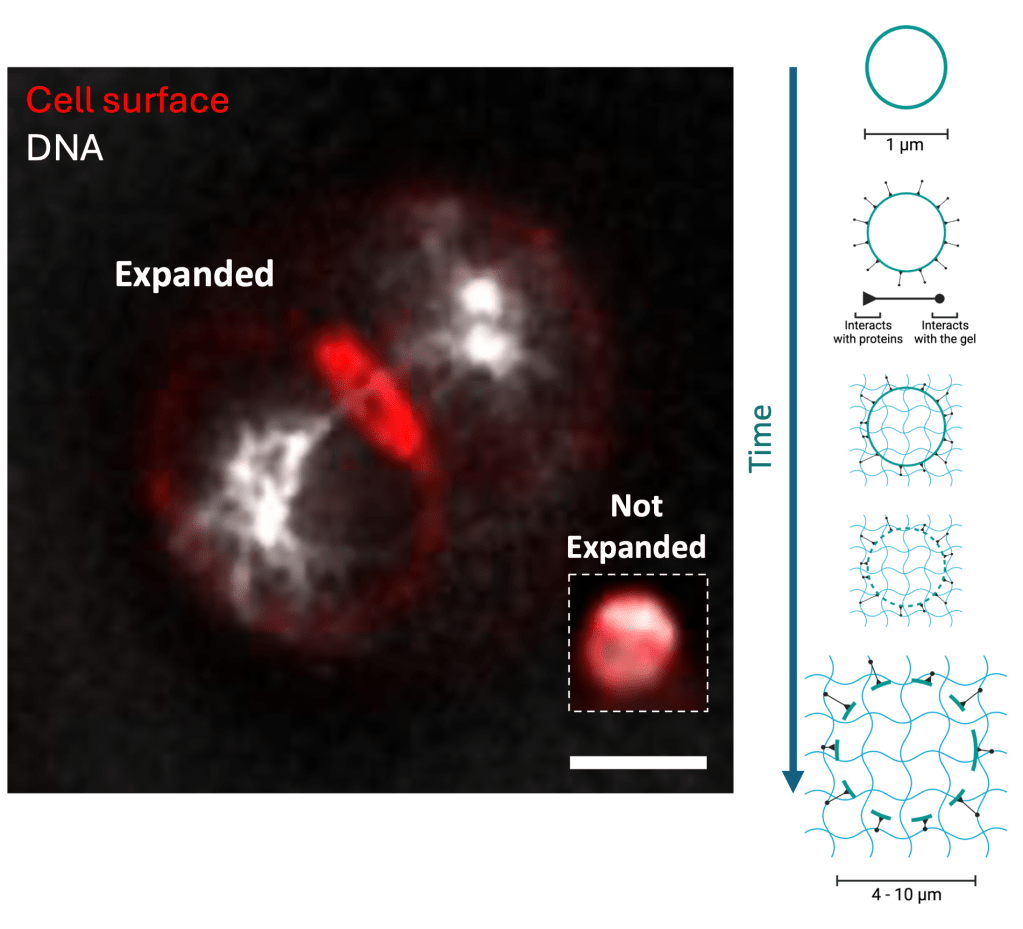
filler
Impact of antibiotics on S. aureus intracellular infection: We are exploring how antibiotics influence the intracellular lifestyle of S. aureus.
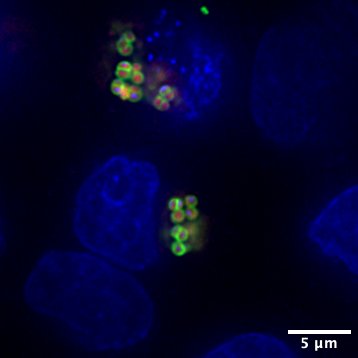
filler
S. aureus-induced host cell reprogramming: How does intracellular S. aureus manipulate host cell pathways to create a favorable environment for its survival and replication?
filler
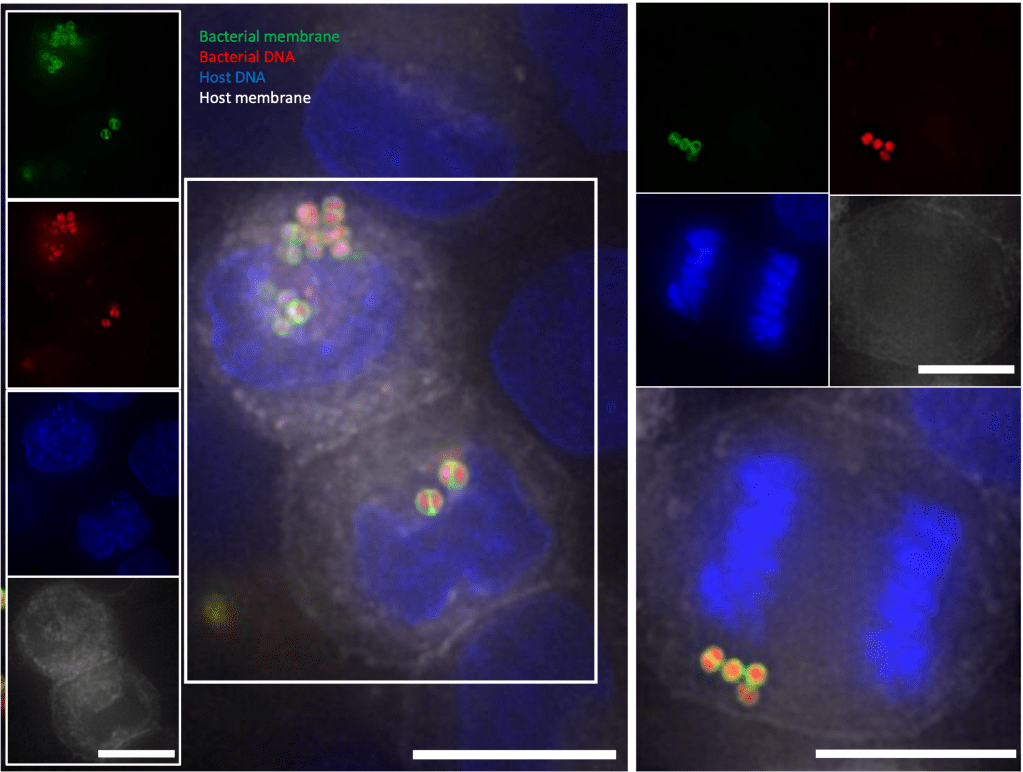
filler
Translational applications of S. aureus research: Ultimately, our goal is to translate our findings into clinical applications. By identifying key bacterial and host factors involved in intracellular infection, we aim to develop new diagnostic tools, therapeutic targets, and antibacterial strategies.
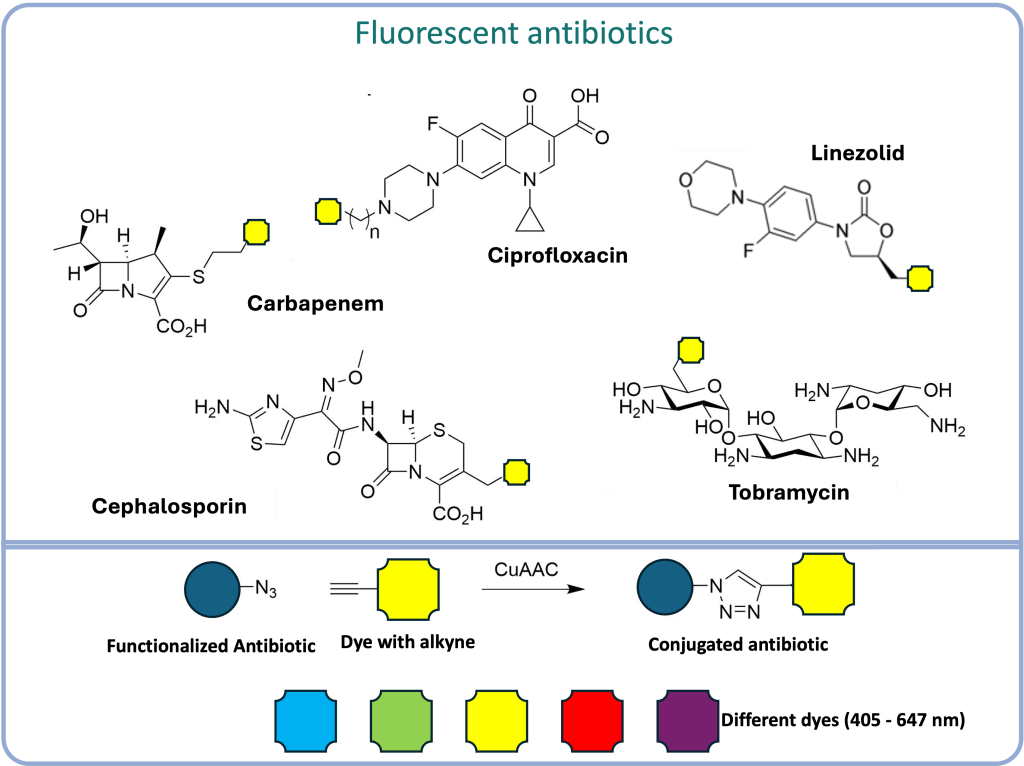
filler
filler
Funding and Support
filler
This work would be impossible without the support of several funding agencies. Thank you!
filler
filler
filler
Collaborators
filler
All our work is based on a wide network of collaborators that make us better! A big thank you to them!!!!